Show Notes 26 May 2023
Story 1: Solar panel efficiency to increase 50% with first production of ‘miracle’ tandem cells – Key trend to watch: using perovskite for solar panels
Source: Yahoo! News Story by Anthony Cuthberston
Link: https://news.yahoo.com/solar-panel-efficiency-increase-50-170539591.html?fr=sycsrp_catchall

- A South Korean firm [Qcells] has announced the world’s first production line for perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells, which promise an increase in efficiency of between 50-75 per cent compared to standard solar panels.
- The commercialization of solar cells that use perovskite follows years of breakthroughs with the mineral, which has been hailed as a ‘miracle material’ for its potential to transform various industries, including renewable energy.
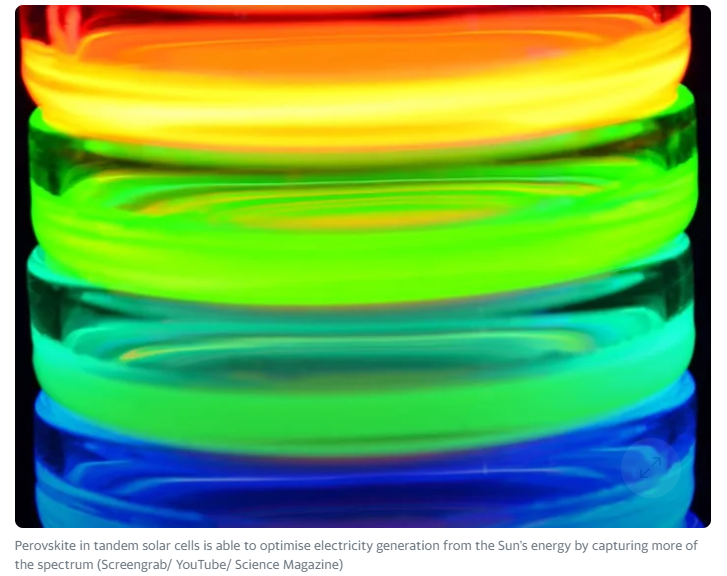
- Side note: Why perovskites could take solar cells to new heights:
- Perovskite is one of the most common crystal structures on the planet. This family of crystalline compounds is at the forefront of research seeking alternatives to silicon. Perovskites are widely seen as the likely platform for next-generation solar cells, replacing silicon because of its easier manufacturing process, lower cost, and greater flexibility.
- Perovskites hold promise for creating solar panels that could be easily deposited onto most surfaces, including flexible and textured ones. These materials would also be lightweight and cheap to produce.
- Side Note: The term perovskite refers not to a specific material, but to a whole family of compounds.
- Perovskite was discovered in 1839 and named after Russian mineralogist L.A. Perovski. Side note source: https://news.mit.edu/2022/perovskites-solar-cells-explained-0715
- Side Note: What is a “tandem” solar panel?
- Tandem solar cells are able to improve the efficiency of standard solar panels by splitting the light spectrum and optimising the harvesting of energy from each section [or layer] into electricity.
- A tandem solar panel consists of 2 solar cells on top of each other. The top cell is made of perovskite. This cell converts part of the solar spectrum into electricity and transmits the infrared light to the bottom silicon solar cell. Source: https://www.tno.nl/en/sustainable/renewable-electricity/advanced-solar-technologies/tandem-technology-higher-pv-performance/
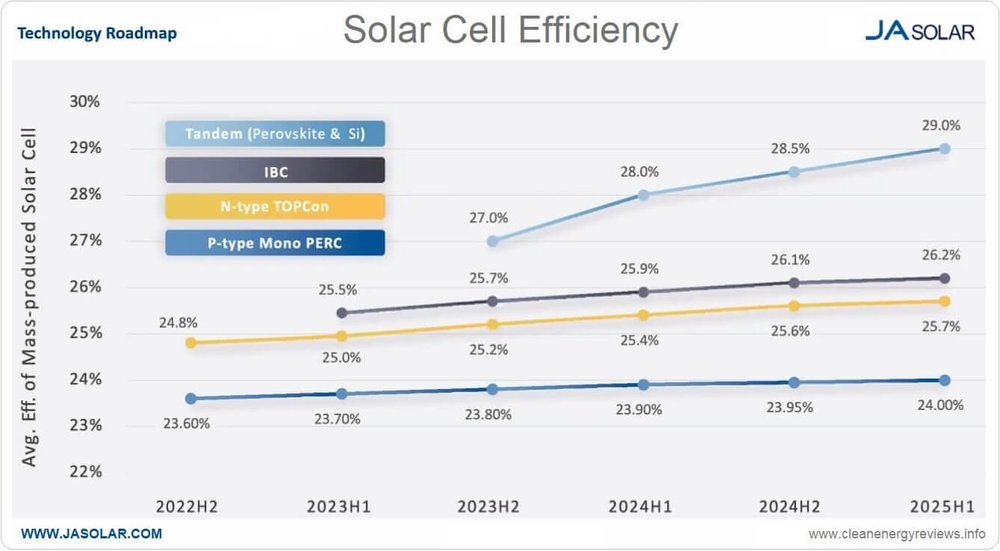
- The current world record for solar cell efficiency is 32.5 per cent – meaning nearly a third of solar radiation is converted into eletrical energy – which was achieved with a perovskite-silicon tandem cell in December.
- By comparison, traditional silicon-based solar cells are currently only capable of reaching around 22 per cent efficiency.
- Qcells said it will invest $100 million to roll out the next-generation solar cell technoloy, which until now has been limited to lab tests and academic research.
- The investment will fund a pilot production line at a factory in South Korea, which is projected to be operational by late next year.
- Additional related news: This Bill Gates-backed technology could be the future of solar power – see: https://interestingengineering.com/innovation/bill-gates-technology-future-of-solar
- A company backed by Bill Gates is aiming to commercialize perovskite panels in order to make solar energy extremely viable. CubicPV, based in Massachusetts and Texas, is supported by Gates’ Breakthrough Energy Ventures.
- The firm is currently engineering new solar panels consisting of a bottom silicon layer and a top perovskite layer resulting in an efficiency of 30 percent.
- This is according to a report by CNBC published on May 20.

Story 2: First-of-its-kind mission makes major discovery about the unknown depths of our oceans
Source: The Cool Down Newsletter Story by Brett Aresco
Source: Saildrone website
Link: https://www.saildrone.com/about

- On our May 5 show we talked about how there are huge gaps in our knowledge of the life forms in the Earth’s oceans. Of the 2.2 million species believed to exist in the Earth’s oceans, only 240,000 have been described by scientists.
- Here’s another mind-blowing factoid noted in this article:
- 80% of the world’s oceans remain unmapped, making it difficult for scientists to understand the full picture of ocean sustainability, topography, and biodiversity.
- Luckily, an American company has set out to change things. California-based technology startup Saildrone — with the help of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) — recently completed a historic, crewless mission to map more than 17,000 square miles of the previously unknown ocean floor around Alaska’s Aleutian Islands and off the California coast.
- The mission was undertaken by the Saildrone Surveyor, which the company calls “the world’s largest uncrewed ocean mapping vehicle.” The vessel took 52 days to map the area around Alaska’s Aleutian Islands before embarking upon its second mission off the California coast.
- The missions, which mapped “high priority” areas across “key regions” in high resolution, yielded unexpected discoveries, such as “a previously unknown seamount standing approximately 1,000 meters [3,200 feet] high.”
- More about Saildrone:
- Per Saildrone’s website: Saildrone designs, manufactures, and operates unmanned sailing vessels.
- The company’s Saildrones are wind and solar-powered autonomous surface vehicles which make cost-effective ocean data collection possible at scale.
- The Saildrone team collects critical marine data, delivered in real-time, from any ocean at any time of year. The team is building the world’s largest high-resolution ocean data sets, working with governments and private companies around the globe.
- The Saildrone vehicles also include an advanced acoustic and camera system that, combined with a proprietary onboard machine learning algorithm, fuses sensor data to deliver significantly expanded information and decision advantage 24/7.
- Saildrone’s patented wing technology was born from 10 years of R&D in pursuit of the land speed record.

Story 3: James Webb telescope spots ancient water frozen in a near-Earth comet — and scientists want to collect it
Source: Live Science via MSN.com Story by Joanna Thompson

- For the first time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has spotted a water-rich comet in the inner solar system, NASA recently announced. The finding may help to solve the long-held mystery of how Earth got its water, the research team said in a study published May 15 in the journal Nature.
- Dubbed Comet Read, the object is surrounded by a haze of gas and dust called a halo. When the James Webb Space Telescope analyzed this halo using a specialized near-infrared instrument that detects heat, it found that the gas was composed largely of water vapor, implying that the comet’s heart likely contains frozen water from the early solar system, potentially originating 4.5 billion years ago. But weirdly, the halo contained virtually no carbon dioxide, a major ingredient in most known comets.
- Comet Read is what’s known as a main belt comet. These rare objects reside inside the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Like regular comets, they are thought to contain ices made up of a wide variety of elements. But unlike most comets, they are only periodically surrounded by a gaseous halo and tail.
- Comet Read’s missing carbon dioxide, however, presents a bigger mystery. It could be that Read, for some reason, simply formed without any CO2. Or it’s possible that it had carbon dioxide early in its life but that the volatile compound burned away over time due to the sun’s heat.
- This discovery offers another clue in the quest to solve where Earth’s plentiful water came from; scientists have long theorized that bombardment from icy comets may have been instrumental in giving Earth its first liquid water billions of years ago, though the question is far from settled.
- According to the researchers, the next step would be to send a probe to the asteroid belt in hopes of collecting physical samples from Comet Read and other main belt comets like it. This could help scientists figure out how water becomes distributed throughout star systems, laying the groundwork for life as we know it.

Story 4: Meta, BMW to Offer In-Car Virtual Reality for Passengers
Source: ExtremeTech.com Story by Josh Norem
Link: https://www.extremetech.com/cars/meta-bmw-to-offer-in-car-virtual-reality-for-passengers


See video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4bhmar2bztA&t=84s
- Meta’s reality lab division is partnering with BMW to explore the possibilities of a virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experience while riding as a passenger in one of its future cars. The two companies have released a video demonstrating their progress so far while also admitting this is not something arriving anytime soon.
- Side note: Reality Labs is a business and research unit of Meta Platforms (formerly Facebook Inc.)
- The short video states that both companies have been aspiring to bring virtual experiences to each other’s audiences for some time now.
- BMW says it started experimenting with Augmented Reality 10 years ago to create not just the ultimate driving machine but the ultimate driving experience.
- Meta says it began its plans for car Virtual Reality in 2021 based on how much time we spend in cars these days.
- In joining together for this project, the companies created a pair of prototype glasses for in-car experiences it calls Project Aria. The glasses have a thick, all-black design, making them appear like a lighter version of the HTC Vive Elite XR.
- The biggest hurdle both companies initially had to overcome was how to track objects while in a fast-moving car, which they say was a problem that had never been previously solved.
- That’s because everything in the vehicle is moving in relation to the VR headset while the car is moving through the world. This means the headset can’t display stable VR content like it typically does in your living room.
- To figure this problem out, Meta connected its Project Aria glasses to a BMW’s sensor array. This allowed Meta engineers to improve the tracking system to understand the device’s location inside the car and where the car is in relation to the outside world.
- This allows projected objects to be anchored inside the car while it’s moving, which they say is a breakthrough. It even allows for the placement of Augmented Reality objects outside the vehicle.