Story 1: New MIT Museum opened on October 2nd – it’s a must see for all geeks!
Source: MIT News Story by Zach Winn
Link: https://news.mit.edu/2022/mit-museum-opening-0930
- Last week my wife and I toured Cape Cod, Nantucket, and Martha’s Vineyard. And we ended our trip with two days in Boston.
- We walked the famous Freedom Trail in downtown Boston, seeing such things as Paul Revere’s home which was built in 1680! So, it was very old when he moved in!
- The Freedom Trail was fascinating, but for me, the real highlight was seeing the new Massachusetts Institute of Technology Museum, which opened earlier this month.
- Here’s the link: https://mitmuseum.mit.edu/
- It’s an ultra-modern 56,000-square-foot facility at the Cambridge campus that documents the Institute’s innovations in science, technology, engineering, arts, and math starting with its founding in 1861.
- The museum’s galleries feature interactive displays that let users do seriously geeky things such as manipulate the genomes of virtual mice, or work with neural networks that learn how to recognize facial expressions.
- I loved it all! In the artificial intelligence exhibit area, I collaborated with an AI computer to compose a poem on-the-fly. That was a very trippy experience!
- Overall, what surprised me was the Museum’s hands-on learning labs and maker spaces, in addition to the sheer number of engaging interactive exhibits.
Story 2: MIT scientists develop robotic capsule to deliver insulin orally
Source: MIT News Story by Anne Trafton
Link: https://news.mit.edu/2022/protein-drugs-gi-tract-0928
- Here’s the problem: Insulin and most other “biologic drugs” — drugs consisting of proteins or nucleic acids — can’t pass through the mucus barrier that lines the human digestive system. So, to date, as we all know, patients must give themselves injections.
- FYI, a biologic drug is a substance that is made from a living organism or its products and is used in the prevention, diagnosis, or treatment of cancer and other diseases. Biological drugs include antibodies, interleukins, and vaccines. Also called biologic agent and biological agent.
- A new robotic drug capsule developed at MIT may one day be able to provide a painless alternative.
- The capsule, which is about the size of a multivitamin, has a robotic cap that spins and tunnels through the mucus barrier when it reaches the small intestine, allowing drugs carried by the capsule to pass into cells lining the intestine.
- The MIT research team recently demonstrated that they could use this approach to successfully deliver insulin orally.
- The Robo-capsule carries its drug payload in a small reservoir at one end and its main body has the features that enable it to tunnel through the mucus barrier in the digestive tract.
- And after it has done its job, the Robo-capsule dissolves. It can do this because the capsule is coated with gelatin that can be tuned to dissolve at a specific pH after delivering the insulin.
- It’s another example of the amazing advancements coming out of MIT every day!
Story 3: Scientists create Algae-Based Microrobots to deliver antibiotics within the lungs
Source: Medgadget.com Story by Conn Hastings
Link: https://www.medgadget.com/2022/09/algae-based-microrobots-deliver-antibiotics-within-lungs.html
See video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OuOr6Dj1Wsw&t=6s
- Researchers at the University of California San Diego have developed a microrobot system to treat bacterial pneumonia.
- The microrobots consist of living algae cells that can swim very effectively in biological fluids, allowing them to navigate throughout the lungs and deliver drugs to difficult-to-reach areas.
- The algae cells are studded with polymer spheres loaded with antibiotics.
- And these polymer spheres are coated with cell membranes from a type of white blood cell [called neutrophils] that acts as your immune system’s first line of defense.
- This helps the algae cells to neutralize inflammatory molecules that are released by bacteria in the lungs, providing a highly targeted and localized anti-inflammatory effect.
- In tests in mice with bacterial pneumonia, the algae microrobots successfully helped to clear the bacterial infection.
- Reality check: All the treated mice survived for at least 30 days, whereas untreated mice died within three days.
Story 4: White House is pushing ahead research to cool the Earth by reflecting back sunlight
Source: CNBC Story by Catherine Clifford
- Back in July we talked about a proposal to fight global warming by assembling in space a massive disk-shaped sunlight shield comprised of thousands of individual balloon-like bubbles.
- Now the administration in Washington wants to explore other ideas.
- Recently the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy announced they are coordinating a five-year research plan to study ways of modifying or reflecting the amount of sunlight that reaches the earth to temper the effects of global warming.
- There are several kinds of remarkable sunlight-reflection [sometimes called solar geoengineering] technologies being considered, including:
- stratospheric aerosol injection
- marine cloud brightening [see video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LLgAZOaK70c]
- and cirrus cloud thinning
- Stratospheric aerosol injection involves spraying an aerosol like sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere to reflect sunlight.
- And because it has the potential to affect the entire globe, this idea often gets the most attention.
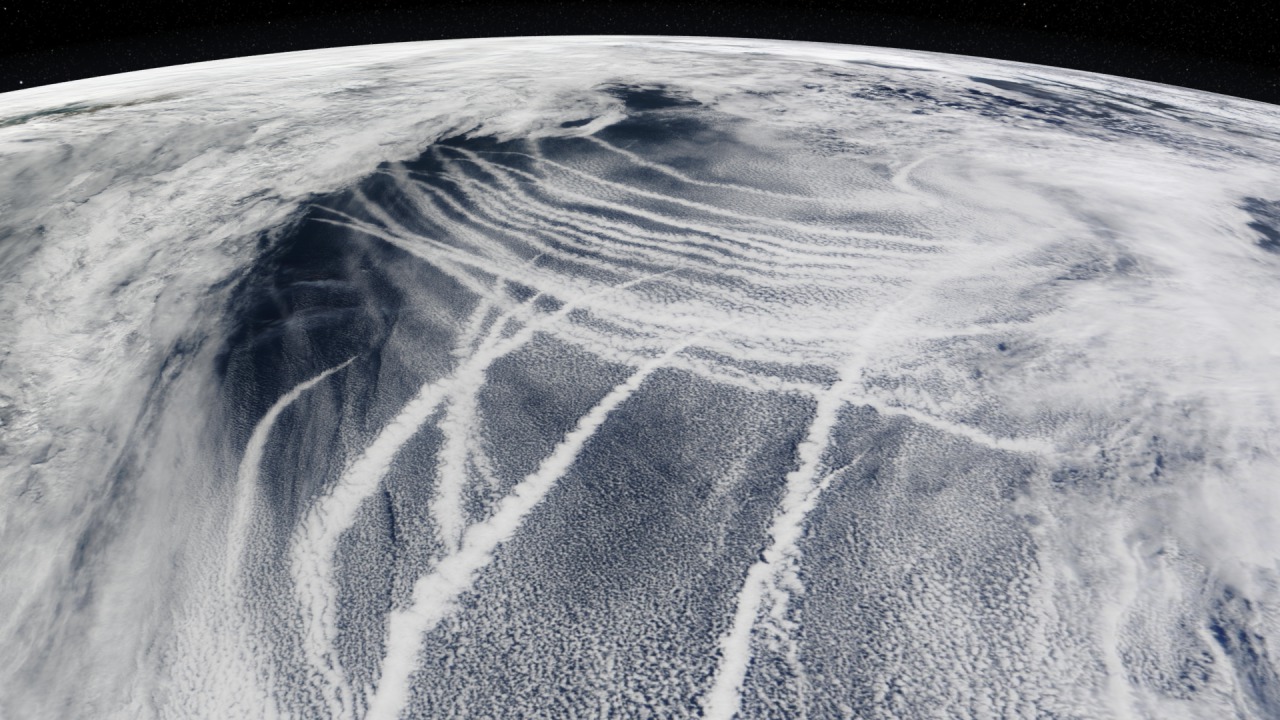
- Marine cloud brightening [also known as marine cloud seeding or marine cloud engineering] is a proposed solar radiation management climate engineering technique that would make clouds brighter, reflecting a small fraction of incoming sunlight back into space to offset global warming.
- Additional information in the show notes all about this [source Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marine_cloud_brightening]
- Today, emissions particles mix with clouds in the atmosphere and increase the amount of sunlight they reflect, reducing warming.
- Marine cloud brightening proposes to generate a similar effect using benign material (e.g., sea salt) delivered to clouds that are most susceptible to these effects (marine stratocumulus).
- Most clouds are quite reflective, bouncing incoming solar radiation back into space.
- Clouds consist of water droplets, and clouds with smaller droplets are more reflective.
- Cloud condensation nuclei are necessary for water droplet formation. The central idea underlying marine cloud brightening is to add aerosols to atmospheric locations where clouds form. These would then act as cloud condensation nuclei, increasing the cloud albedo.
- The marine environment has a deficit of cloud condensation nuclei due to lower levels of dust and pollution at sea, so marine cloud brightening would be more effective over the ocean than over land. In fact, marine cloud brightening on a small scale already occurs unintentionally due to the aerosols in ships’ exhaust, leaving ship tracks.
- Cirrus Cloud Thinning is a proposal which aims to eliminate or thin high-altitude wispy clouds made of ice crystals to allow heat to escape into space.
- So, it will be interesting to see in five years which approach is deemed the best to pursue.